Amir2000 Image Automation | Case Study
A local-first desktop pipeline that converts high-volume photo sets into deterministic filenames, review-ready metadata, and publish-ready website assets with a human approval gate.
0. Section Map (What Each Point Means)
This map explains the purpose of each numbered section so any reader can quickly understand where to find business, product, and engineering context.
- 1: Executive summary and delivery snapshot.
- 1A: Live catalog data snapshot for scale, QC distribution, and camera mix.
- 2: Problem landscape and operational pain points.
- 3: Objectives and real-world constraints.
- 4: Solution architecture at a glance.
- 5: End-to-end workflow, including post-review publish path.
- 6: Operator UX and quality gate behavior.
- 7: Engineering decisions and reliability safeguards.
- 8: Stack boundaries and technical ownership.
- 9: Tradeoffs, roadmap, and ML planning.
- 10: Deep-dive documentation map for implementation details.
Why this matters by audience:
- Recruiters: clear ownership story from problem to shipped workflow.
- Managers: explicit risk controls, quality gate, and operational maintainability.
- Developers: concrete architecture, modules, state model, and extension points.
1. Executive Summary
The automation solves a practical production problem: moving from manual, error-prone image publishing to a repeatable, auditable pipeline where every image has explicit lifecycle state in a database.
- Built as a Windows desktop workflow orchestrated by
main_set.py. - Improves naming quality from generic labels to more specific subject naming (for example flower/bird/animal-level context where possible).
- Improves caption and keyword accuracy while reducing manual typing errors.
- Uses SQLite (
review.db) as operational truth for queue, status, and auditability. - Publishes approved assets through FTP + MySQL upsert and syncs to local mirror DB.
- Scale context: about 32,000 images were uploaded manually before this automation; since mid-2025, close to 10,000 images have been processed through the automated workflow.
1A. Live Data Snapshot (Current Catalog)
To complement the narrative, this snapshot reads live from MySQL table photos_info_revamp and shows scale,
quality mix, and camera evolution. This is intentionally a compact data view to support the story without overwhelming it.
Catalog rows
42,429
Largest QC band
Good (18,392 / 43.3%)
Top camera volume
Canon EOS 5D Mark IV (19,637)
Cumulative Growth (Live)
QC Status Distribution
Camera Mix by Year (Top 5)
Interactive charts are unavailable right now. This usually means the Chart.js CDN was blocked by browser/network filtering.
Live source: photos_info_revamp. The charts show catalog evolution and quality mix, not an exact automation start date.
2. Problem Context
Manual workflows worked for small sets, but failed at scale. The pain points were not isolated bugs; they were system-level reliability issues.
- Naming was often too generic and did not identify subject type clearly enough (for example specific flower, bird, or animal context).
- Manual batch grouping prioritized throughput but frequently missed quality consistency.
- Filename consistency, safe character handling, and collision prevention were difficult to enforce manually.
- Any correction was painful because fixing one mistake required touching multiple files/fields manually.
- No single source of truth for state transitions from import to publish.
Concrete before/after naming examples
Before (more generic naming/caption context)
After (more specific subject/location naming and cleaner metadata context)
3. Objectives And Constraints
Primary objectives:
- Deterministic naming and duplicate prevention.
- Repeatable, staged workflow with clear status transitions.
- Higher-quality naming/caption/keyword output with less generic metadata.
- Human-in-the-loop publishing decisions.
- Publish integration with existing website storage and MySQL model.
Constraints:
- Local-first operation on Windows desktop environment.
- Existing website data model and path conventions must be preserved.
- No silent production writes without manual validation.
4. Solution Overview
The system is organized as a guided multi-stage pipeline. Operational state is stored in SQLite, and publish is a deliberate final step from the review editor.
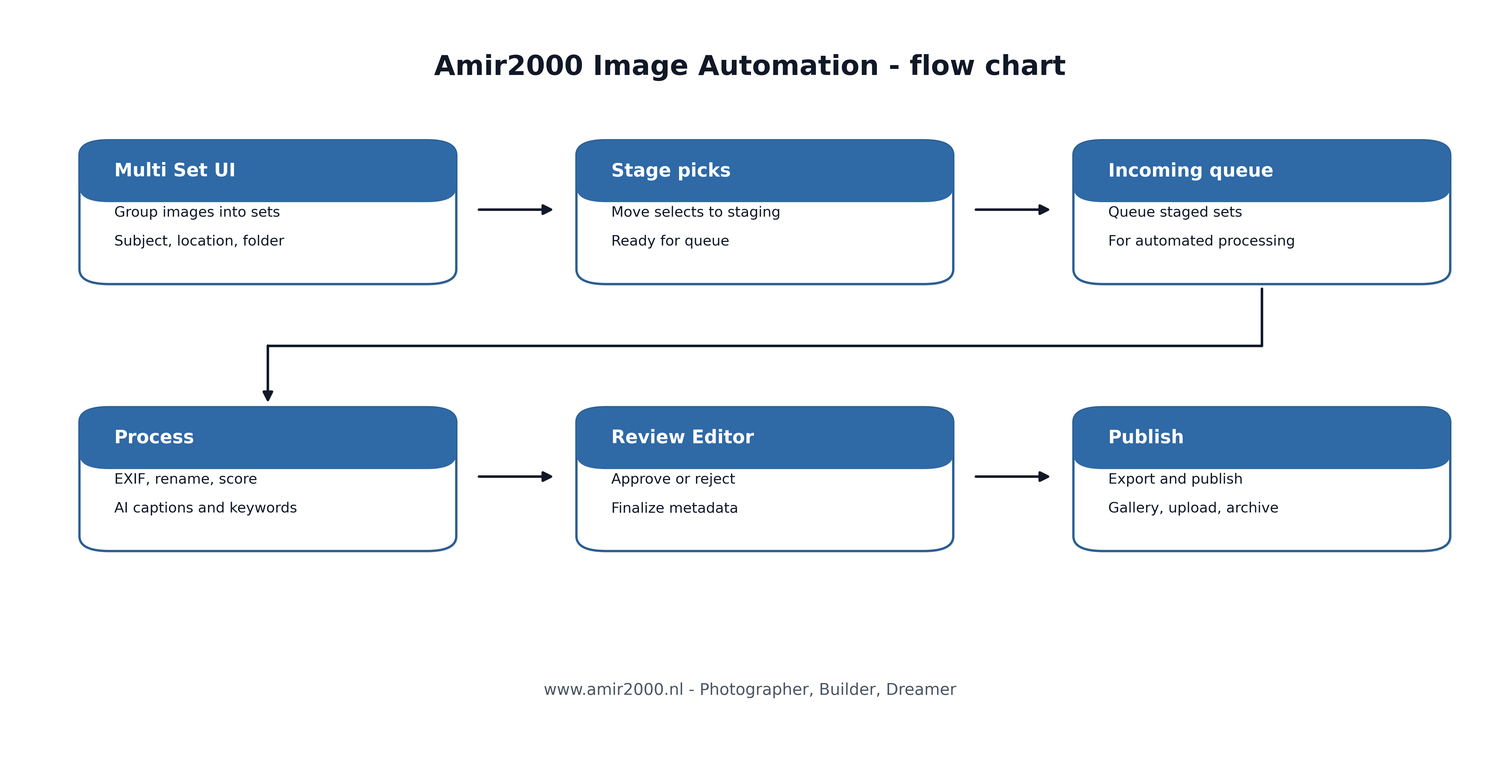
Figure 1: End-to-end flow chart used as architecture overview.
5. Workflow Walkthrough (Stage By Stage)
The production stage list implemented in main_set.py:
- Validate sets: sanity checks before any data mutation.
- Prepare DB and copy to incoming: establish working context and staged inputs.
- Extract EXIF and initial metadata: seed technical metadata and base fields.
- Insert/refresh review rows: create or update
review_queuerecords. - AI quality scoring: compute quality metrics and initial quality classification.
- Resize for Ollama: generate temporary model inputs and set
ollama_path. - Caption/keywords prefill: local LLM suggestions for caption, alt text, and keywords.
- Open review editor: enter the human decision phase.
After the review editor opens (release path):
- Review and edit each row for caption, alt text, keywords, filename, and quality fields.
- Set each row status to Approved or Rejected based on final human judgment.
- Trigger publish for Approved rows only.
- Uploader sends full + thumbnail assets to FTP destinations.
- Uploader performs MySQL upsert by
File_Nameand syncs local mirror IDs. - On clean publish, temp Ollama paths are cleaned and final statuses are persisted.
- Operator validates logs and website output as final QA.
Correction flow is intentionally fast: when a result is not good enough, reject can reverse the item path so it can be redone cleanly for better output.
Runtime failure handling is also rollback-oriented. If a blocking error occurs (for example caption model missing), the session rollback restores files and releases reserved filenames so the run can be safely retried.
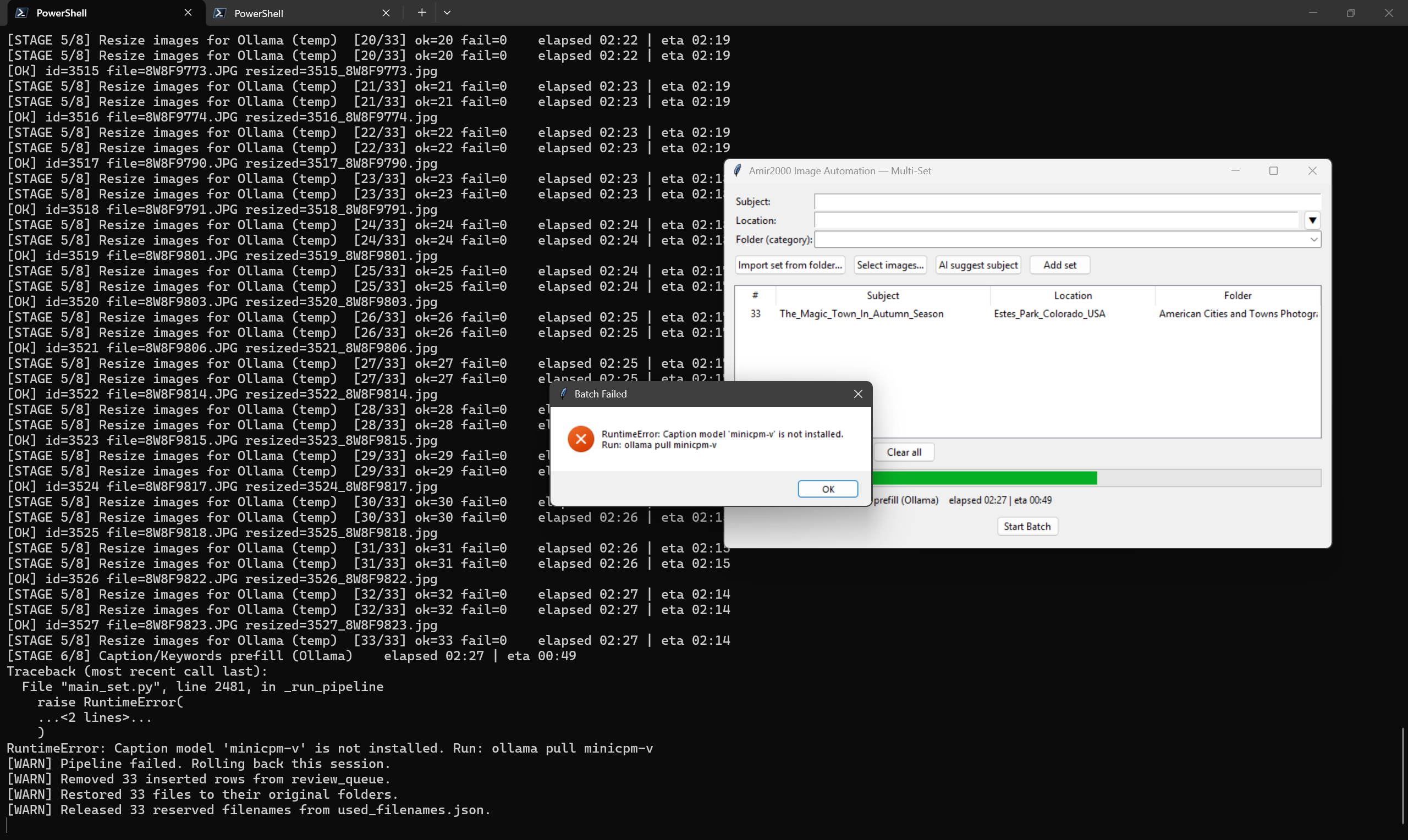
Figure 2: Real rollback event after caption-stage model error, showing session cleanup and filename reservation release.
The result is a controlled transition from raw files to reviewed records to published assets.
6. Operator Experience And Review Gate
The Multi-Set interface is designed for batch processing with visible stage progression and explicit review decisions.
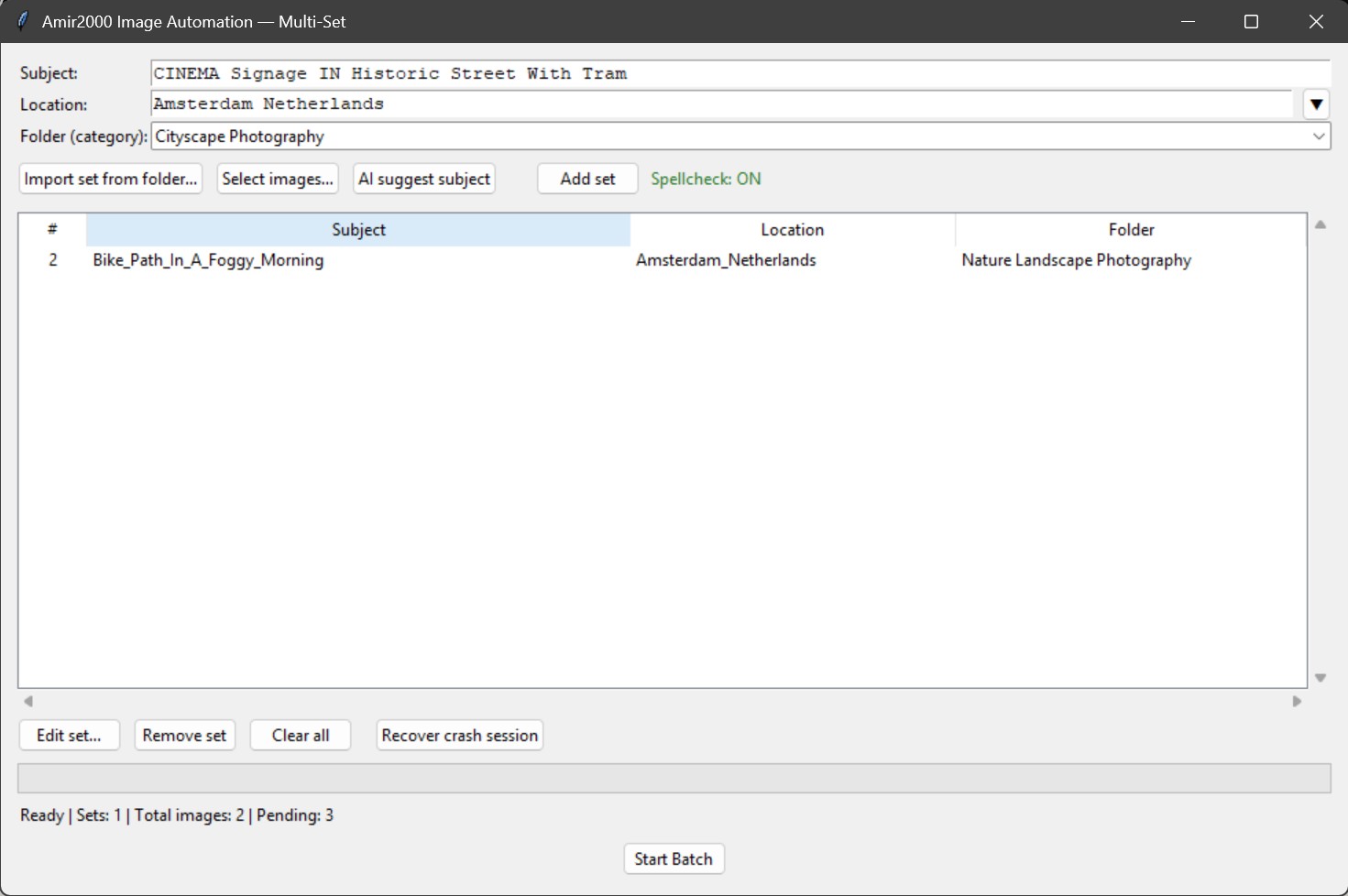
Figure 3: Multi-set operator UI used to run stages and enter review workflow.
- AI output is assistive only.
- Queue management UX was improved with clearer control spacing (fewer accidental clicks between AI suggest and add-set actions).
- The multi-set window is resizable and the queue table supports scrolling so large runs can be reviewed without truncating rows.
- Crash/session continuation is operator-visible: Recover crash session restores saved sets and pending files from the last checkpoint.
- Add-set stability guardrails were added: AI subject suggestion runs single-flight, and runtime callback crashes are captured in
data/crash_runtime.logfor fast diagnosis. - Review editor now includes image position context (Image n/x) to keep large approval sessions trackable.
- Review editor is the mandatory quality and publish gate.
- Only approved rows proceed to upload and DB synchronization.
7. Key Engineering Decisions
- DB as truth:
review_queueinreview.dbtracks lifecycle state. - Filename reservation ledger:
data/used_filenames.jsonprevents duplicate collisions across runs. - Input sanitization and deterministic file naming: reduces manual naming mistakes and unwanted characters in final outputs.
- Keyword context guardrails: geography keywords are context-bound to row taxonomy; unrelated location noise is filtered.
- Local-first AI: Ollama inference for privacy/control; no hard cloud requirement for core processing.
- Publish idempotency: MySQL upsert keyed by
File_Name, not queue row id. - Failure visibility: explicit statuses and logs (
logs/latest_run.log,logs/db_uploader.log). - Runtime compatibility hardening: EXE stage scripts use isolated helper staging and explicit Python 3.13 runtime pinning support.
- Recovery-aware flow: cleanup and rollback paths for interrupted runs and reserved names.
8. Stack And Ownership
- Runtime: Python 3.13, Tkinter, Pillow, sqlite3.
- AI/quality: Ollama local inference, NIMA/BRISQUE/CLIP aesthetic scoring path.
- Data/publish: SQLite operational DB + MySQL/FTP publish integration.
- Ops tooling: PowerShell scripts for setup, preflight, build, pack, and sanitization.
9. Tradeoffs, Roadmap, And ML Planning
Current tradeoffs:
- Single-operator desktop model is simpler and safer, but not multi-user collaborative by design.
- Human review increases quality and safety, but introduces manual approval effort.
- Local model execution improves control/privacy, but depends on local hardware performance.
Explicit non-goals (scope boundaries):
- Not a cloud SaaS or shared multi-user editing platform.
- Not a full enterprise DAM replacement.
- Not a fully autonomous AI publisher that bypasses manual QA.
- Not a generic ingestion platform for arbitrary media types.
Next platform steps:
- Keep scaling automated throughput beyond current ~10,000 image baseline while maintaining quality controls.
- Further caption diversity and weak-output rewrite tuning.
- Richer per-run analytics for quality and failure patterns.
- Additional hardening around publish validation and rollback ergonomics.
ML planning track:
- Build a benchmark set from reviewed rows and editor corrections for repeatable model evaluation.
- Compare candidate caption models on quality, duplication rate, and correction effort per row.
- Introduce confidence thresholds to auto-flag weak outputs for priority human review.
- Use edit history to drive active-learning style prompt/rule improvements per subject/location cluster.
- Add drift monitoring so quality regressions are detected before production-scale runs.
10. Deep-Dive Documentation Map
To keep documentation focused and professional, the deep dive is reduced to a core sequence. These are the pages that matter most, in the order readers should follow from Step 0 to Step 5.
- Step 0: Documentation overview - master index and reading paths.
- Step 1: Purpose and scope - why the system exists and where boundaries are.
- Step 2: Workflow - exact stage-by-stage runtime flow.
- Step 3: Runbook - daily operation and incident recovery.
- Step 4: Database model - source-of-truth tables and state transitions.
- Step 5: Developer guide - safe extension points and implementation guardrails.
Supporting references (optional by need)
- Reference 1-2: Install and setup + User guide.
- Reference 3-4: Troubleshooting + Logging and failure handling.
- Reference 5-6: Data contracts + File reference.
- Reference 7-8: Design principles + Diagrams.